(4-5 mins read)
Introduction & why this article:
We all have been encountering Large-Language models (LLMs) or Generative AI in recent times. This is the foundational model to which the revolutionary ChatGPT, Claude-3, Llama-2/3, Mistral (all text-to-text based) & even the recent one Sora (a text-to-video) to name a few, are based upon.

With multiple breakthroughs in the world of AI, especially after LLMs launch, out of curiosity & to avoid the infamous FOMO, I started to learn this technology, unravelling the core principles that drive LLMs.
While the web is flooded with resources in various formats, decoding the same from first principles is what makes a difference.
This article is my attempt to break down the complex world of AI from its core principles. And moving forward, I aim to explore other key components of AI in layman’s terms, bridging the gap between complex concepts and the everyday world. So, stay tuned with AIpods.co.
Decoding this Digital Brain:
Imagine an LLM as a digital brain, loaded with billions of parameters, akin to our brain neurons. For example: GPT-4(1.76 Trillions), LLaMA-2 (70 Billions). And these models are trained on multiple layers (analogous to the neurons of the human brain).
Now, with a vast number of parameters, why do these models work so well- what is present inside the model which is revolutionary & a game changer for them ?
The reason is “Transformer”, the heart (architecture) of LLMs; And inside Transformer, one word “Attention” and today’s article is about that only.
Introducing Attention – in simple words
When you read a book, our brain intuitively gives attention to certain words to understand the long context & connect the events. And this is what the attention mechanism enables the computer model to focus on certain words that helps it to predict the output or understand the input context.
This revolutionary paper: “Attention is all you need” – By Ashish Vaswani & fellow scientists, paved the way for its success. And this is my humble attempt to make the topic accessible to a much larger audience by breaking such a complex & sophisticated mechanism into layman terms with relatable examples so that you will have a fun journey in reading this rather than feeling puzzled.
Attention through example
Imagine starting a new phase in college. Each student has unique goals & characteristics, much like your fellow batchmates who are joining the same class. Some want to do MBA or MS, some are fond of travelling, drinks & the list goes on. They bring their own set of individual characteristics.
Let’s try to depict this scenario visually.
Consider 7 characteristic parameters/goals of each individual, represented in a matrix [Q] with dimensions [6 x 7] (6 rows x 7 columns), capturing the individuality of Monika, Phoebe, Chandler, Rachael, Ross, and Joey as illustrated in table 1 below:
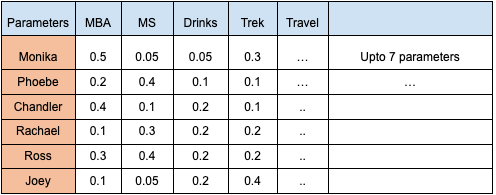
Table 1 (Values are random but depicts their interests towards different parameters)
Now, as the college session kicks off, natural bonds form. Those with similar tastes connect effortlessly.
Let me take an example of Monika who wants to do MBA & is fond of trekking. While she interacts with all, consequently, she will form closer bonds with Chandler (characteristics of MBA match) & Joey (characteristics of trekking match). On a similar note,other students form bonds with each other.
So, in your classroom batch of 6 students:
- Some become close friends.
- Some start formally interacting.
- Some still have no or least interaction.
Now, if we want to visualise just Monika’s interaction, it will look like below:
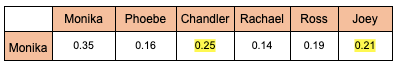
*Values are calculated based on dot product multiplication (to be explained in part 2)
You will observe that her interaction score is maximum with people of similar traits (shown as highlighted).
In a similar manner, we can do the same with all students. Let’s name it as [R] matrix as illustrated in table 2 below:
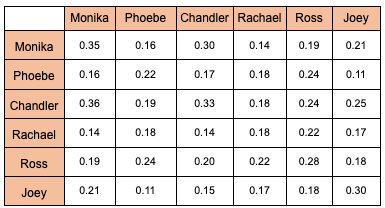
Table 2 (Values are calculated based on dot product multiplication: to be explained in part 2)
The Final Matrix
Now, Monika, after living in proximity to her batchmates, will develop the revised characteristics. Let’s represent it as per below matrix:

And in a similar manner, other students will also get their characteristics revised.
Let’s represent the above in the updated matrix [T] (table 3). Notice that all their characteristics’ scores are revised.
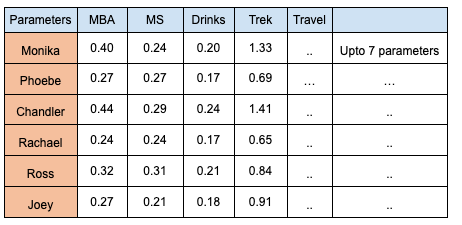
Table 3 (The mathematics will be explained in part 2)
So, the entire attention mechanism looks like:
Interpretation of [T] Matrix & unveiling the attention mechanism:
The values in the transformed [T] matrix indicate the degree to which everyone has acquired traits from others. These values not only represent individual characteristics but also capture the essence of interactions.
In the world of Transformers, the attention mechanism calculates interactions of each word (called tokens in LLMs) with other words, & hence assigns weights (scores) to each interaction, determining how much focus should be given to any text in relation to others.
Summary
In summary, the analogy of students in a classroom helps illustrate the attention mechanism in language models. The model processes input text, understands word dependencies, assigns probability scores to words based on their interactions, and predicts the next word.
If you want to understand this through video, you can visit this link on AI Pods youtube channel.
Understanding the attention mechanism is crucial for comprehending the workings of LLMs. However, you may guess that this entire process of attention is not this straightforward & there are various additional elements & mathematical operations involved to achieve the goal of each table 1, 2 & 3 representation. I will cover those concepts in my upcoming articles starting with attention formula & multi-head attention. Stay tuned !
References:
Transformers Explained – By Umar Jamil
Transformer & Attention series by Serrano Academy
Illustrated Transformer by Jay Allamar

Leave a comment